Triona again leads the way for Oslo municipality
Triona won the procurement “Survey and planning of road and street maintenance” for Oslo municipality. The assignment is to photograph Oslo municipality’s 1365 km of roads and streets including pedestrian and bicycle lanes, register all the data in the Norwegian national road database (NVDB) as well as define a road maintenance plan for Oslo municipality.
We completed the same assignment for Oslo municipality in 2021 and look forward to starting this exciting and comprehensive work and once again collaborate with Oslo municipality. Rune Wilhelm Dragsnes, CEO Triona AS
The new agreement is more extensive and covers the period 2024-2027 and involves several stages of photographing and registration as well as producing a plan for future road maintenance in Oslo municipality.
Since 2021 Triona has further developed processes and software so the work can be carried out in an even more secure and streamlined way. The solution is modular and can be customised according to requirements as regards to photographing, data registration, and the road masterplan.
The main purpose of photographing the roads is to use the result as a base for a road maintenance plan for Oslo’s municipal roads. We need to be able to view the condition of all types of road sections which we manage, and as well see what may need to be replaced or improved. Agency for Urban Environment operations and maintenance
The new and updated process for data collection is shown in the diagram below and can be divided into five process steps: data collection, data processing, registration and verification, common data platform and infrastructure owners.
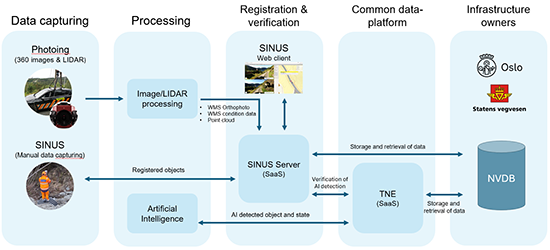
Data collection
For data collection, improved methodology and equipment from the last round of data collection for Oslo municipality will be used. The camera system consists of 6 cameras, LIDAR, dual GPS which are calibrated to deliver optimal images, exact positioning, and identification of road objects such as road signs.
Processing
The system collects two different types of data: 360° panorama images and LIDAR data. These are processed with custom software and are then displayed in a web application. Artificial intelligence (AI) is used to detect objects and road conditions.
Registration and verification
After the 360° images and LIDAR data have been collected, processed, and stored, the data will be registered and validated. Typical work tasks which are carried out are:
- AI-detected data will be reviewed manually in order to eliminate potential errors.
- Based on images and LIDAR data it will be possible to register data based on triangulation.
- Verification that all mandatory and other defined properties are correct.
- For Oslo municipality there are already many objects which are already registered and it is very important that these are not registered as duplicates which would make the data for the master plan incorrect. Triona will therefore update existing objects instead of creating new objects.
- When all quality controls have been done, the objects will be finalized and stored permenantly in the NVDB.
SINUS is used when registering and validating the data. SINUS has many functions for working with this type of data. SINUS works among other things with different types of basemaps, for example orthophoto or state data and manages all data types in the NVDB. Data can also be displayed in different list views so multiple objects can be changed simultaneously and in different forms of combined views.
Common data platform
Transport Network Engine (TNE) is a powerful platform developed by Triona and is used primarily to import AI-data and link data to the road network. In addition, TNE will ensure that all data matches the Norwegian Public Roads Administration’s data catalogue structure before the data is stored in the NVDB.
Infrastructure owners
In this delivery Oslo municipality and the Norwegian Public Roads Administration will be regarded as infrastructure owners. For the Norwegian Public Roads Administration they will ensure that the data is delivered in the correct format and specification according to the data catalogue definition. Triona currently manage the data together with Capgemini which puts us in a unique position to be able to resolve all challenges which may occur when handling this type of data.
More information on the solution can also be found here:




